Hardware Recommendations for Autodesk Revit
These hardware recommendations – covering CPU, video card, and more – will help you configure the right type of system for your next Revit workstation.
Revit System Requirements
Quickly Jump To: Processor (CPU) • Video Card (GPU) • Memory (RAM) • Storage (Drives)
Like most software developers, Autodesk maintains a list of system requirements for Revit that can be used to help ensure the hardware in your system will work with their software. However, this “system requirements” list only covers the very basics of what hardware is needed to run the software, not what hardware will actually give the best performance. Because of how inconsistent those lists can be, we’ve taken the time to perform testing to determine what hardware run Revit he best. Based on this testing, we have come up with our own list of recommended hardware for Revit.
Processor (CPU)
When it comes to CPUs there are two main specifications that define the capability of a CPU:
- The frequency directly affects how many operations a single CPU core can complete in a second (how fast it is).
- The number of cores is how many physical cores there are within a CPU (how many operations it can run simultaneously).
Whether a high frequency or high core count CPU is better depends on how well a program is designed to take advantage of multiple CPU cores (often referred to as multi-threading).
What is the best CPU for Autodesk Revit?
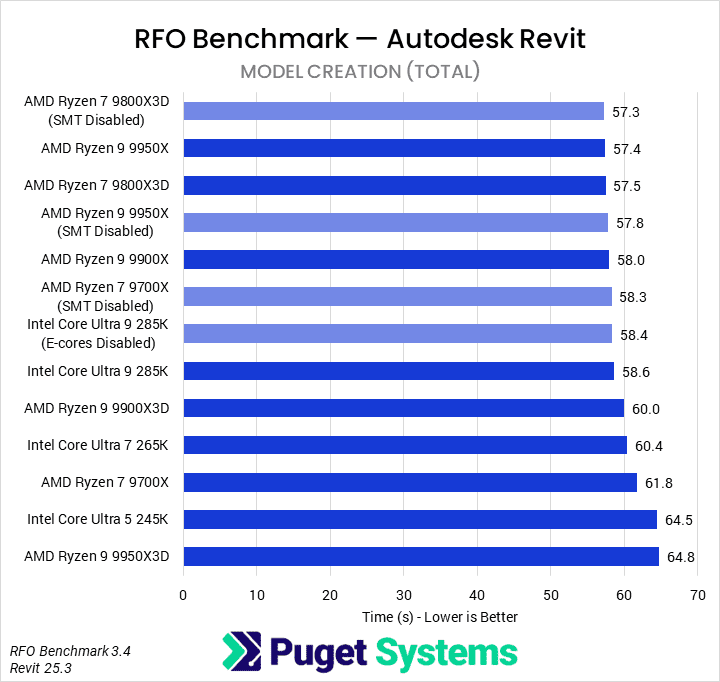
The majority of design tasks in Revit is only able to utilize a single CPU core which makes a high frequency CPU – regardless of the core count – an ideal choice for these tasks. Because of this, our Revit Modeling & Design workstation uses AMD’s Ryzen™ processors, which offer high clock speeds alongside a good number of cores (for multitasking, etc). In particular, the Ryzen 7 9800X3D offered the best performance in our testing.
If you want to improve your rendering times, however, we suggest using a CPU with an even higher number of cores. The Autodesk Raytracer (ART) rendering engine included in Revit can benefit greatly from using a CPU with more cores, so upgrading to the Ryzen 9 9950X is an easy way to boost that performance. Alternatively, we offer other workstations with even higher core counts that are more focused on rendering, if that is your priority. It may also be worth considering a GPU-based rendering engine instead, but either way, you can check out our rendering recommended systems for more options.
Does having more CPU cores improve Revit performance?
Designing and modeling in Revit is not able to utilize more than a handful of cores. In our testing, we found that a CPU with a high operating frequency will give you the best overall performance for general modeling tasks. Rendering, however, can see moderate to large performance gains with a higher core count CPU. Revit’s built-in rendering is largely being replaced by GPU-based plug-ins, though, so if rendering is a big part of your workflow please contact our consultants to get a configuration tailored to your specific needs and budget.
Do I need a Xeon CPU for Revit?
In the past, Intel Xeon® CPUs were more robust than their Core-series counterparts. Today, however, there is very little functional difference between the two Intel product families for software like Revit. In addition, Xeon CPUs are almost always clocked lower than their Core Ultra CPUs or AMD’s Ryzen models – which means that you will be giving up some amount of performance to gain a set of features that are typically only useful for servers.
Should I get an overclocked system for Revit?
In general, we do not recommend overclocking for any professional workstation. Typically, the modest performance gains are not worth the downsides associated with overclocking which can include instability, shorter hardware lifespan, and potential data inaccuracies.
Video Card (GPU)
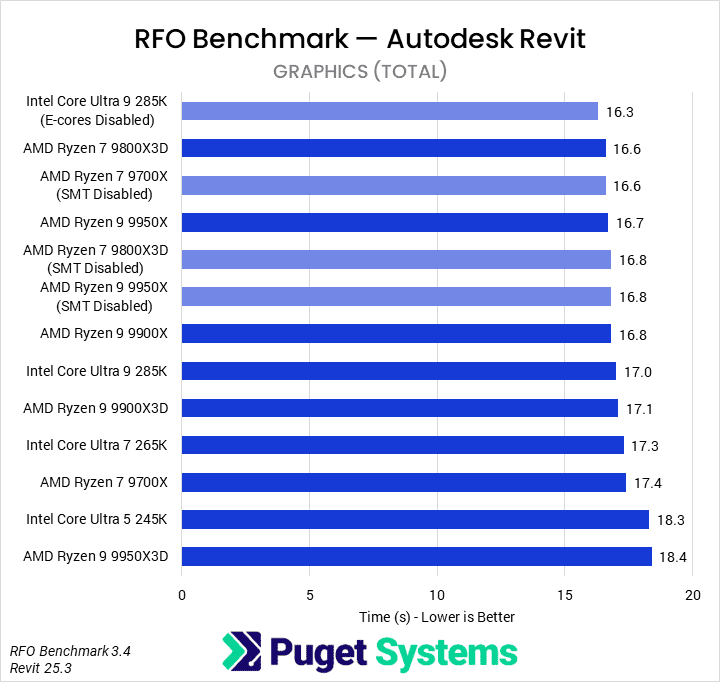
When working with models in Revit, the video card is solely used to display the model on the screen. While a more powerful video card may allow the model to be drawn at a higher FPS (frames per second) when rotating, zooming, or panning around the model, the video card requirements for Revit are relatively low.
What is the best video card for Autodesk Revit?
For most users, a mid-range professional card such as the NVIDIA RTX PRO™ 4000 Blackwell will be more than powerful enough. If you plan to use a GPU-based rendering engine within Revit, consider the more powerful RTX PRO™ 4500 or 5000 Blackwell models, or potentially even multiple video cards.
Between consumer and professional video cards, Autodesk’s official policy used to be that they “only recommend and support the professional NVIDIA Quadro and AMD FirePro graphics family cards” – but for some applications, like Revit, that guidance seems to have softened. NVIDIA has also moved away from the Quadro brand name, and transitioned to RTX PRO™, which is what our recommended systems now default to. However, in some situations (such as VR visualization) a consumer GeForce card may be a better option. But be aware that these consumer cards are not quite as reliable as the professional cards and may not always have official Autodesk support.
Do I need to use an RTX PRO (formerly Quadro) card for Revit or is GeForce okay?
Autodesk used to only certify Revit to run on a short list of tested video cards, which were primarily Quadro models – though that brand name has been replaced by NVIDIA RTX PRO™. However, recent versions of Revit no longer have a list of certified video cards! Current Autodesk guidelines indicate that any high-performance video card with a minimum amount of VRAM should work, so for most users a GeForce card will likely be just fine. The main reason to go for an RTX PRO model are increased reliability, more VRAM, and better compatibility with other applications you may use alongside Revit (including other Autodesk products that still have hardware certification).
Memory (RAM)
How much system memory (RAM) does Autodesk Revit need?
While the exact amount of RAM you need is going to depend on your particular projects, for Revit we generally recommend 64GB. This should allow you to open and work with a single project with a file size of up to at least 2GB without any issues and to do some multitasking with other programs like Photoshop or 3ds Max. If you work with even larger models, or tend to have Revit running alongside even more demanding applications, you may want to consider upgrading to 96GB of RAM or even more.
Storage (Drives)
What is the best type of drive to use for Autodesk Revit?
Thanks to their speed and relatively affordable price, we strongly recommend solid-state drives (SSDs) for the primary drive that will host your OS and the installation of Revit itself. The high speed of SSDs allows your system to boot, launch applications, and load files many times faster than any traditional hard drive. In particular, the newer NVMe type of SSDs utilize the latest connections like M.2 and offer the fastest transfer rates.
If your budget allows, it is also a very good idea to have a second SSD that can be used to store your active projects to further decrease load and save times. We highly recommend using an OS drive with a capacity of least 500GB to ensure you do not need to upgrade your primary drive (which is often a complicated process) in the near future.
Will a solid-state drive help me open and save assemblies faster in Revit?
Yes! SSDs are much faster than traditional hard drives and in many cases can give a noticeable decrease in the time it takes to open and save projects. SSDs also impact the overall responsiveness of a computer, and since Revit files are not very large even a mid-size SSD should have plenty of capacity.
What sort of drive is best for data storage and backup?
Since SSDs are still more expensive than platter drives per GB, for long term storage and backup we recommend using a traditional hard drive or even an external drive array. Network attached storage systems are a great way to go for that, as they can be shared between multiple workstations and usually offer features to provide some level of data redundancy (protection against losing files if one of the drives dies).