Hardware Recommendations for Redshift
Here at Puget Systems, we have tested a wide range of video cards with Redshift so that we could put together the following recommendations for the fastest rendering workstation hardware.
Puget Labs Certified
These hardware configurations have been developed and verified through frequent testing by our Labs team. Click here for more details.
Redshift System Requirements and Benchmarks
Quickly Jump To: Processor (CPU) • Video Card (GPU) • Memory (RAM) • Storage (Drives)
Like most applications, the system requirements for Redshift can be found on their official website. They also have a good FAQ, which primarily focuses on GPU compatibility and performance. Since their information is split into two sections like that, and since it may tend a bit toward the minimum requirements rather than best specs, we have put together our own hardware recommendations below.
Is Redshift a CPU or GPU based rendering engine?
Redshift is a fully GPU-based rendering engine. This means that the video cards (or GPUs) in your system are what impacts how long renders take to complete, rather than the CPU.
Processor (CPU)
What type of CPU does Redshift need?
In Redshift, as well as most other GPU-based engines, the CPU does not play a direct role in the process of rendering scenes. It does have a small impact on the time spent loading a scene, but that is pretty minimal in the grand scheme of things. However, if you are also using the same system for modeling or animation – in a program like Cinema4D, Maya, or 3ds Max – then you will want a CPU with a high clock speed in order to ensure good performance in those applications. On the other hand, if you also use CPU based rendering engines then having a higher core count would benefit those programs… but it will not improve Redshift’s rendering speed.
Aside from raw performance, it is also important to consider the number of PCI-Express lanes a CPU supports. This will govern how many video cards can be used, which has a big impact since video cards are the primary driver for rendering performance in Redshift.
What is the best CPU for Redshift?
As mentioned above, the CPU itself isn’t going to directly contribute to Redshift’s rendering – but it will determine how many video cards the system can support, which does impact performance. Here are a couple of our recommendations:
- AMD Ryzen 7 7700X 8 Core – This is one of the highest clock speed CPUs available, and does very well with both Redshift and modeling / animation applications. It has enough PCI-Express lanes to support dual video cards, along with other standard hardware devices (NVMe drives, etc).
- AMD Threadripper PRO 7965WX 24 Core – AMD’s Threadripper PRO processors have far more PCI-Express lanes than more consumer-oriented models. Combined with the right motherboard, this CPU can allow up to four video cards in a single tower workstation. The trade-off is that the platform as a whole is more expensive, but being able to fit three or four high-end GPUs in a single system is worthwhile in many workflows.
Will a more powerful CPU help at all in Redshift?
A faster CPU will allow you to extract mesh data, load textures, and prepare scene data more quickly, but it will make no impact on how long it takes each individual render to complete. We recommend going for a high clock speed CPU without worrying about core count – and without spending too much money there, instead focusing your budget on more powerful GPUs (and/or more of them).

This should only show up on small and below
Video Card (GPU)
How does Redshift utilize video cards (GPUs)?
As mentioned above, the video card selection is the driving factor for performance in Redshift. The faster the better, and you can also use multiple GPUs to further speed up rendering.
There are two aspects of a video card that impact render capabilities: the raw speed of the GPU itself and the amount of memory on the card. Video memory will limit how large and complex of scenes can be rendered effectively, though Redshift does support “out of core” rendering which will allow system memory to be used if there is not enough dedicated GPU memory available… but that comes with a reduction in speed, so it is best to get video cards with enough RAM onboard if at all possible. GeForce cards tend to have good raw performance, with decent amounts of video memory, while Quadro cards come with larger amounts of VRAM but also cost more for the same level of raw performance.
What are the best video cards (GPUs) for Redshift?
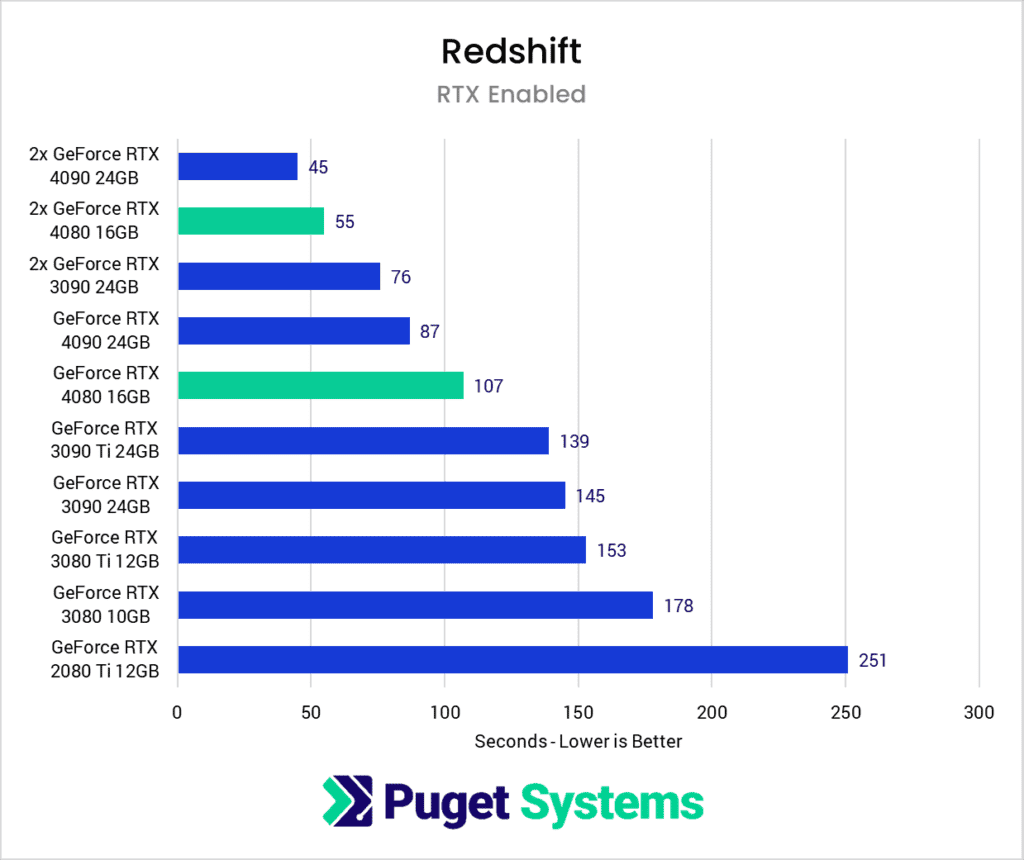
- GeForce RTX 4080 16GB – A great choice if you want just one or two video cards and don’t work with overly complex scenes.
- GeForce RTX 4090 24GB – Our go-to recommendation for most GPU rendering customers, the RTX 4090 provides the best performance in Redshift while also having a tremendous 24GB of memory.
- NVIDIA RTX A5000 24GB – For those who want to stack several video cards in the same system, NVIDIA’s professional GPUs are a solid option. The RTX A5000 is the top-end card that can be installed in a set of four in large tower chassis and still be within the limits of a 1600W power supply. If you need even more memory, the RTX 6000 Ada Generation has 48GB of VRAM but is far more expensive and may be limited to two or three GPUs.
Should I use a professional video card for Redshift?
It is also important to remember NVIDIA’s professional-grade video cards, as they can be a better choice than GeForce cards for some users. They do cost more, but for that increased price you get several benefits:
- Higher VRAM options – up to 48GB on the RTX A6000 and 6000 Ada
- Better multi-GPU support – thanks to the use of blower-style cooling systems and more constrained power consumption
- ECC memory on higher-end models – for increased stability
Does Redshift support multiple GPUs? Do they need to be in SLI?
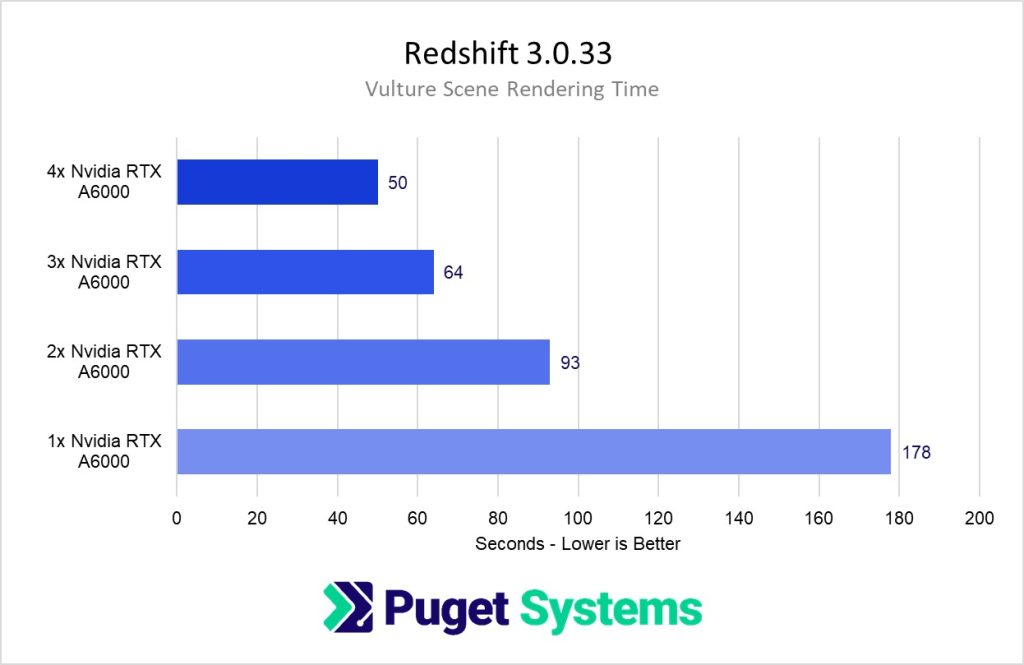
Yes! Redshift scales very well with multiple cards and can significantly improve your render times. However, since it is using the cards for compute purposes they do not need to be in SLI mode. In fact, SLI can sometimes cause problems so we recommend leaving it disabled if possible.
How well does Redshift scale across multiple video cards (GPUs)?
Redshift scales well across multiple video cards, but the cooling systems on most GeForce models are not designed with multiple GPUs in mind. For the best overall performance, variants with a single fan that exhausts heat out the back (commonly called “blower” cards) are ideal – and most NVIDIA “professional” cards use such cooling systems. Stacking a few of those will give fantastic rendering performance, though it does require a larger chassis, strong power supply, and plenty of airflow from the case fans.
Is it better to spend money on a higher number of total GPUs, or more powerful GPUs, for Redshift?
From a pure cost/performance perspective, it is almost always better to use a higher number of more affordable GPUs rather than using one or two more expensive GPUs. However, the downside to this approach is that your workstation will be physically larger, louder, hotter, and use more power than a system with fewer, but more powerful cards. In addition, if your renders require a higher amount of VRAM (video card memory) you may be forced into using more expensive cards that have more VRAM.
Can I mix and match different models of video cards for Redshift?
As long as each card is supported, Redshift does allow you to mix and match different models of video cards. We do this for some customers who need a primary Quadro video card due to a different program’s hardware requirements, but want to utilize GeForce cards to improve rendering performance. However, the more different the cards (different architectures, different versions of CUDA, etc.) the larger the chance of errors occurring. Also note that if the cards have different amount of VRAM you will be limited to the smallest amount.
Do I have to use NVIDIA cards for Redshift or can I use AMD?
For a long time, Redshift only worked with CUDA which is proprietary to NVIDIA video cards. However, starting with version 3.5.15, support has been added for AMD cards as well.
Do I need to use a Quadro card for Redshift or is GeForce okay?
NVIDIA’s professional GPUs, formerly known as “Quadro” cards, work just fine for Redshift – but for the majority of the users they are not worth the much higher price. From a performance perspective GeForce cards are just as fast while being many times cheaper. Due to the large difference in cost, with the same budget you can generally get faster rendering performance by sticking with GeForce cards – at least up to a point.
However, there are certain times where you may want to use “professional” cards. If you need more VRAM than what is available on the GeForce cards, RTX A-series cards have up to twice the VRAM which allows for much higher resolution and detailed scenes to be rendered without running out of video memory. They are also slightly more reliable long-term since they are designed to operate under heavy load for extended periods of time. If those factors are a concern for you, simply select that type of cards on the configure page instead.
Recent Redshift GPU Articles:
Memory (RAM)
How much system memory (RAM) does Redshift need?
While the exact amount of RAM you need is going to depend on your particular projects, for Redshift (and GPU rendering in general) we generally recommend a minimum of 32GB. That should be plenty for dedicated rendering boxes, but our systems do support more for those who need it. If you tend to have several different applications open and running at the same time – like Maya, Cinema 4D, After Effects, etc. – then you might want 64GB or even more.
Storage (Hard Drives)
What is the best type of drive to use for Redshift?
Thanks to their speed and relatively affordable price, we strongly recommend solid-state drives (SSDs) for the primary drive that will host your OS and the installation of Redshift itself – along with any other software you use. The high speed of SSDs allows your system to boot, launch applications, and load files many times faster than any traditional hard drive. In particular, the newer NVMe type of SSDs utilize the latest connections like M.2 and offer the fastest transfer rates.
If your budget allows, it is also a very good idea to have a second SSD that can be used to store your active projects to further decrease load and save times. We highly recommend using an OS drive with a capacity of at least 500GB to ensure you do not need to upgrade your primary drive (which is often a complicated process) in the near future.
What sort of drive is best for data storage and backup?
Since SSDs are still more expensive than platter drives per GB, for long-term storage and backup we recommend using a traditional hard drive or even an external drive array. Network attached storage systems are a great way to go for that, as they can be shared between multiple workstations and usually offer features to provide some level of data redundancy (protection against losing files if one of the drives dies).



